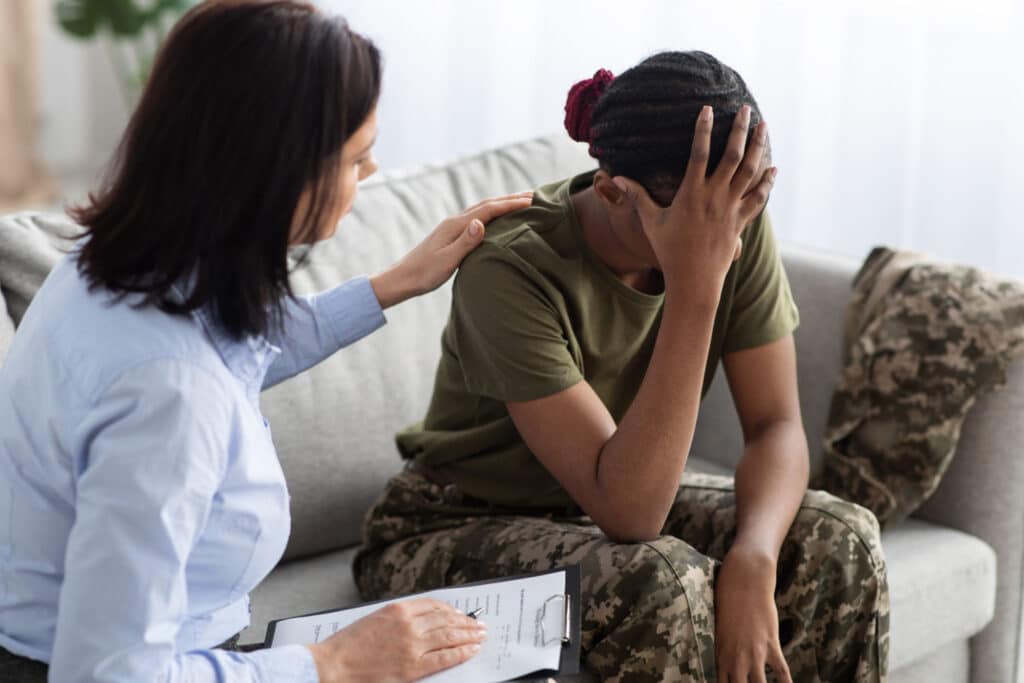
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a complex mental health condition that can develop after exposure to traumatic events such as violence, natural disasters, accidents, or military combat. While PTSD affects individuals differently, modern medicine and psychology offer a wide range of evidence-based treatments that help people regain stability, confidence, and quality of life.
Understanding available treatment paths empowers individuals and families to make informed decisions and seek timely care.
Understanding PTSD and Its Impact
PTSD is not simply a reaction to stress. It involves persistent changes in how the brain processes fear, memory, and emotional regulation.
Common Symptoms of PTSD
-
Intrusive memories such as flashbacks or nightmares
-
Avoidance behaviors related to trauma reminders
-
Negative mood changes, including guilt or emotional numbness
-
Hyperarousal, such as irritability, insomnia, or heightened startle response
When left untreated, PTSD may interfere with relationships, work performance, and physical health.
Medical Treatment Approaches
Medical interventions primarily focus on symptom stabilization and restoring emotional balance. These treatments are often combined with psychotherapy for optimal outcomes.
Prescription Medications for PTSD
Medications can reduce symptom severity and improve daily functioning.
Commonly prescribed options include:
-
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) to manage anxiety and depression
-
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) for mood regulation
-
Sleep-support medications for trauma-related insomnia and nightmares
Medication plans are individualized and monitored closely to minimize side effects.
Role of Ongoing Medical Supervision
Regular follow-ups ensure medications remain effective while adjusting dosages as symptoms evolve. Medical care also addresses related concerns such as chronic pain, fatigue, or substance use disorders.
Psychotherapeutic Treatment Paths
Therapy is the foundation of long-term PTSD recovery, helping individuals process trauma safely and rebuild emotional resilience.
Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT)
This structured approach helps patients identify distorted thought patterns linked to trauma and replace them with healthier coping strategies.
Key benefits include:
-
Reduced fear responses
-
Improved emotional control
-
Stronger problem-solving skills
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
EMDR supports the brain’s natural healing process by reprocessing traumatic memories while engaging bilateral stimulation.
It is particularly effective for individuals who struggle to verbally describe traumatic experiences.
Prolonged Exposure Therapy
This method gradually reduces avoidance by safely exposing individuals to trauma-related memories and triggers in controlled settings.
Over time, the brain learns that these reminders are no longer dangerous.
Complementary and Holistic Therapies
Many individuals benefit from combining traditional therapy with holistic approaches that support mind-body healing.
Mindfulness and Stress Regulation Practices
-
Meditation and breathwork
-
Yoga-based trauma recovery programs
-
Grounding techniques for emotional regulation
Lifestyle-Based Support
-
Regular physical activity
-
Balanced nutrition to support brain health
-
Consistent sleep routines
These methods enhance therapy outcomes and improve overall well-being.
Integrated Treatment Models
The most effective PTSD care often involves a multidisciplinary approach, combining medical care, psychotherapy, and lifestyle support.
Integrated models emphasize:
-
Personalized treatment plans
-
Collaboration between mental health professionals
-
Long-term follow-up and relapse prevention
Recovery is not linear, and treatment plans evolve as healing progresses.
Barriers to Treatment and How to Overcome Them
Despite effective treatments, many individuals delay seeking help due to stigma or lack of access.
Common challenges include:
-
Fear of judgment
-
Limited mental health resources
-
Financial constraints
Telehealth services, community programs, and trauma-informed care initiatives are expanding access and reducing these barriers.
The Path Toward Recovery
PTSD is treatable. With proper support, individuals can reclaim control over their thoughts, emotions, and future. Healing does not erase the past but allows people to move forward with strength, insight, and renewed purpose.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long does PTSD treatment usually take?
Treatment duration varies, but many individuals see improvement within several months of consistent therapy.
2. Can PTSD be cured completely?
While PTSD may not disappear entirely for everyone, symptoms can be significantly reduced and well-managed.
3. Is medication always necessary for PTSD?
No. Some individuals recover with therapy alone, while others benefit from medication support.
4. Are PTSD treatments effective for childhood trauma?
Yes. Trauma-focused therapies are effective across age groups, including childhood and developmental trauma.
5. Can PTSD symptoms return after treatment?
Symptoms may resurface during high stress, but learned coping strategies help manage recurrence.
6. Is group therapy helpful for PTSD?
Group therapy can reduce isolation and provide shared understanding, especially for trauma survivors.
7. When should someone seek professional help for trauma symptoms?
If symptoms persist longer than a month or interfere with daily life, professional support is strongly recommended.